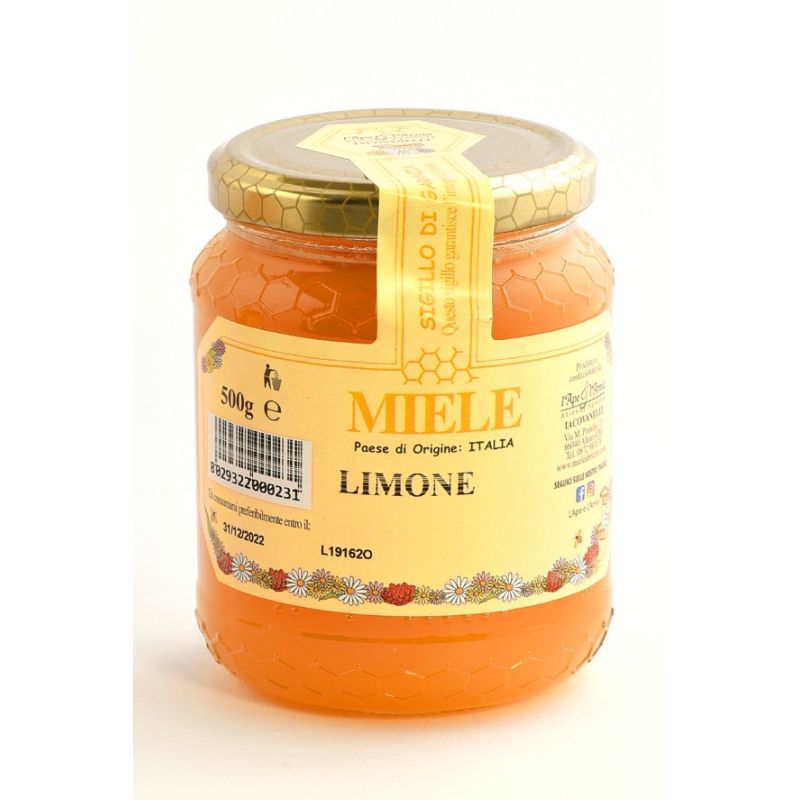
MIEL DE LIMÓN 500 g, el producto puede aparecer cristalizado. La miel de limón es de color ámbar oscuro cuando está líquida, más claro cuando está cristalizada; tiene un aroma y un sabor suaves y afrutados y es muy apreciada en tés e infusiones. País de origen :ITALIA Condiciones de conservación: conservar a temperatura ambiente en un lugar seco.
El proceso de cristalización de la mielCualquier miel puede cristalizar, excepto la miel de acacia, la miel de castaño y las mieles de mielada, que no suelen cristalizar. Cuando la miel contiene más glucosa que fructosa, es más probable que cristalice. La cristalización comienza cuando las moléculas de glucosa se agregan para formar cristales. Estos cristales se extienden por la miel, dando a la solución una consistencia más espesa y granulosa. La velocidad y el alcance de la cristalización dependen de varios factores, como la temperatura y la composición de la miel.
El proceso de cristalización de la mielCualquier miel puede cristalizar, excepto la miel de acacia, la miel de castaño y las mieles de mielada, que no suelen cristalizar. Cuando la miel contiene más glucosa que fructosa, es más probable que cristalice. La cristalización comienza cuando las moléculas de glucosa se agregan para formar cristales. Estos cristales se extienden por la miel, dando a la solución una consistencia más espesa y granulosa. La velocidad y el alcance de la cristalización dependen de varios factores, como la temperatura y la composición de la miel.
El proceso de cristalización de la mielCualquier miel puede cristalizar, excepto la miel de acacia, la miel de castaño y las mieles de mielada, que no suelen cristalizar. Cuando la miel contiene más glucosa que fructosa, es más probable que cristalice. La cristalización comienza cuando las moléculas de glucosa se agregan para formar cristales. Estos cristales se extienden por la miel, dando a la solución una consistencia más espesa y granulosa. La velocidad y el alcance de la cristalización dependen de varios factores, como la temperatura y la composición de la miel.
El proceso de cristalización de la mielCualquier miel puede cristalizar, excepto la miel de acacia, la miel de castaño y las mieles de mielada, que no suelen cristalizar. Cuando la miel contiene más glucosa que fructosa, es más probable que cristalice. La cristalización comienza cuando las moléculas de glucosa se agregan para formar cristales. Estos cristales se extienden por la miel, dando a la solución una consistencia más espesa y granulosa. La velocidad y el alcance de la cristalización dependen de varios factores, como la temperatura y la composición de la miel.
El proceso de cristalización de la mielCualquier miel puede cristalizar, excepto la miel de acacia, la miel de castaño y las mieles de mielada, que no suelen cristalizar. Cuando la miel contiene más glucosa que fructosa, es más probable que cristalice. La cristalización comienza cuando las moléculas de glucosa se agregan para formar cristales. Estos cristales se extienden por la miel, dando a la solución una consistencia más espesa y granulosa. La velocidad y el alcance de la cristalización dependen de varios factores, como la temperatura y la composición de la miel.
El proceso de cristalización de la mielCualquier miel puede cristalizar, excepto la miel de acacia, la miel de castaño y las mieles de mielada, que no suelen cristalizar. Cuando la miel contiene más glucosa que fructosa, es más probable que cristalice. La cristalización comienza cuando las moléculas de glucosa se agregan para formar cristales. Estos cristales se extienden por la miel, dando a la solución una consistencia más espesa y granulosa. La velocidad y el alcance de la cristalización dependen de varios factores, como la temperatura y la composición de la miel.
El proceso de cristalización de la mielCualquier miel puede cristalizar, excepto la miel de acacia, la miel de castaño y las mieles de mielada, que no suelen cristalizar. Cuando la miel contiene más glucosa que fructosa, es más probable que cristalice. La cristalización comienza cuando las moléculas de glucosa se agregan para formar cristales. Estos cristales se extienden por la miel, dando a la solución una consistencia más espesa y granulosa. La velocidad y el alcance de la cristalización dependen de varios factores, como la temperatura y la composición de la miel.